The Role of Probiotics in Children’s Health: Addressing Colic and Digestive Issues
Probiotics have gained recognition for their potential health benefits, particularly in children. As beneficial bacteria that support gut health, probiotics may play a crucial role in addressing common childhood issues such as colic and digestive problems. This article explores how probiotics can benefit children’s health, focusing on their impact on colic and various digestive issues.
1. Understanding Probiotics and Their Importance in Children’s Health
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. They play a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for proper digestion, immune function, and overall health.
- Gut Microbiome Development: The gut microbiome in infants and children undergoes significant changes during the early years of life. Factors such as mode of delivery (vaginal vs. cesarean), diet (breastfeeding vs. formula), and antibiotic use can influence the development of the gut microbiome.
- Immune System Support: A balanced gut microbiome is crucial for the development of the immune system. Probiotics can help modulate immune responses, reducing the risk of infections and allergies in children.
2. Probiotics and Colic in Infants
Colic is characterized by excessive crying and fussiness in infants, typically occurring in the first few months of life. The exact cause of colic is unknown, but digestive discomfort is often suspected.
- Mechanisms of Action: Probiotics may help alleviate colic symptoms by:
- Improving Gut Health: Probiotics can help balance gut bacteria, promoting better digestion and reducing gas and bloating, which may contribute to colic symptoms.
- Modulating Inflammation: Some studies suggest that probiotics can reduce inflammation in the gut, potentially alleviating discomfort and crying associated with colic.
- Research Insights: Several studies have reported that specific probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus reuteri, can significantly reduce crying time and improve overall well-being in colicky infants.
3. Probiotics for Digestive Issues in Children
Digestive issues are common in children and can range from mild discomfort to more serious conditions. Probiotics may offer relief for several digestive problems, including:
- Constipation: Probiotics can help improve bowel regularity by enhancing gut motility and increasing the frequency of bowel movements. Strains such as Bifidobacterium lactis have been shown to be effective in alleviating constipation in children.
- Diarrhea: Probiotics can help manage diarrhea, particularly antibiotic-associated diarrhea and viral gastroenteritis. They work by restoring the balance of gut bacteria and enhancing the gut’s ability to absorb fluids. Strains like Saccharomyces boulardii are commonly recommended for preventing and treating diarrhea in children.
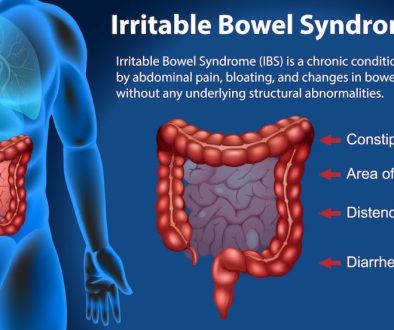
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Some children experience IBS, characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits. Probiotics may help alleviate symptoms by improving gut motility and reducing inflammation. Certain strains, such as Lactobacillus plantarum, have shown promise in clinical studies.
4. Choosing Probiotics for Children
When selecting probiotics for children, consider the following factors:
- Specific Strains: Look for products that contain well-researched strains proven effective for children’s digestive health. Strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Lactobacillus reuteri are often recommended.
- CFU Count: The colony-forming units (CFUs) indicate the number of viable bacteria in a probiotic. Aim for products with a CFU count that is appropriate for your child’s age and health needs.
- Formulation: Probiotics for children come in various forms, including powders, chewable tablets, and liquid drops. Choose a formulation that is easy for your child to take and palatable.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before introducing probiotics into your child’s routine, consult a pediatrician or healthcare provider. They can help determine the best strains and dosages based on your child’s specific needs.
5. Incorporating Probiotics into a Child’s Diet
In addition to supplements, probiotics can be included in a child’s diet through various food sources:
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, and certain cheeses contain live cultures that can provide beneficial probiotics. Choose plain, unsweetened options to avoid added sugars.
- Prebiotic Foods: Incorporating prebiotic-rich foods, such as bananas, garlic, onions, and whole grains, can help support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to promote overall health and well-being.
Probiotics offer a promising approach to supporting children’s health, particularly in managing colic and digestive issues. By promoting a balanced gut microbiome and enhancing digestive function, probiotics can contribute to improved comfort and well-being in children. Incorporating probiotics through diet and supplements, along with consulting a healthcare professional, can provide a holistic approach to addressing digestive concerns in young ones.